Science spotlights: Difference between revisions
From CSDMS
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
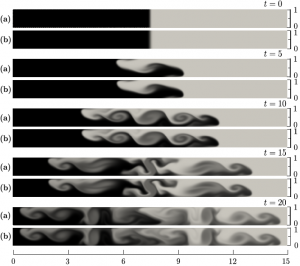
|bgcolor="gray" align="left"| Comparison of the gravity current concentration fields (white corresponds to c=0 and black to c=1) in a sloping channel with ''θ'' = 15° and ''Re<sub>H</sub>'' = 750, obtained via two different numerical approaches. a): present immersed boundary approach, b): coordinates aligned with containter walls (Birman et al. (2007)). Good agreement is observed even for the small scales of the concentration field. The darker region is the maximum concentration. | |bgcolor="gray" align="left"| Comparison of the gravity current concentration fields (white corresponds to c=0 and black to c=1) in a sloping channel with ''θ'' = 15° and ''Re<sub>H</sub>'' = 750, obtained via two different numerical approaches. a): present immersed boundary approach, b): coordinates aligned with containter walls (Birman et al. (2007)). Good agreement is observed even for the small scales of the concentration field. The darker region is the maximum concentration. | ||
|} | |} | ||
More text will follow.... | |||
Revision as of 14:36, 9 November 2010
Science spotlights
TURBINS: Simulation of Gravity and Turbidity Currents
| Comparison of the gravity current concentration fields (white corresponds to c=0 and black to c=1) in a sloping channel with θ = 15° and ReH = 750, obtained via two different numerical approaches. a): present immersed boundary approach, b): coordinates aligned with containter walls (Birman et al. (2007)). Good agreement is observed even for the small scales of the concentration field. The darker region is the maximum concentration. |
More text will follow....