2023 CSDMS meeting-073: Difference between revisions
From CSDMS
Xiedanghan (talk | contribs) Created page with "{{CSDMS meeting personal information template-2023 |CSDMS meeting first name=Danghan |CSDMS meeting last name=Xie |CSDMS meeting institute=Boston University |CSDMS meeting city=Boston |CSDMS meeting country=United States |CSDMS meeting state=MA |CSDMS meeting email address=danghan@bu.edu }} {{CSDMS meeting select clinics1 2023 |CSDMS_meeting_select_clinics1_2023=2) Best practices open source Python-based infrastructure }} {{CSDMS meeting select clinics2 2023 |CSDMS_meeti..." |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 71: | Line 71: | ||
{{CSDMS meeting abstract template 2023 | {{CSDMS meeting abstract template 2023 | ||
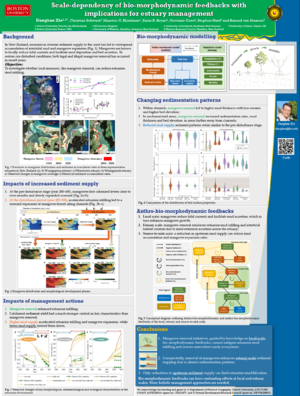
|CSDMS meeting abstract=Changes in upstream land-use have significantly transformed downstream coastal ecosystems around the globe. Restoration of coastal ecosystems often focuses on local-scale processes, thereby overlooking landscape-scale interactions that can ultimately determine restoration outcomes. Here we use an idealized bio-morphodynamic model, based on estuaries in New Zealand, to investigate the effects of both increased sediment inputs caused by upstream deforestation following European settlement and mangrove removal on estuarine morphology. Our results show that coastal mangrove removal initiatives, guided by knowledge on local-scale bio-morphodynamic feedbacks, cannot mitigate estuarine mud-infilling and restore antecedent sandy ecosystems. Unexpectedly, removal of mangroves enhances estuary-scale sediment trapping due to altered sedimentation patterns. Only reductions in upstream sediment supply can limit estuarine muddification. Our study demonstrates that bio-morphodynamic feedbacks can have contrasting effects at local and estuary scales. Consequently, human interventions like vegetation removal can lead to counterintuitive responses in estuarine landscape behavior that impede restoration efforts, highlighting that more holistic management approaches are needed. | |CSDMS meeting abstract=Changes in upstream land-use have significantly transformed downstream coastal ecosystems around the globe. Restoration of coastal ecosystems often focuses on local-scale processes, thereby overlooking landscape-scale interactions that can ultimately determine restoration outcomes. Here we use an idealized bio-morphodynamic model, based on estuaries in New Zealand, to investigate the effects of both increased sediment inputs caused by upstream deforestation following European settlement and mangrove removal on estuarine morphology. Our results show that coastal mangrove removal initiatives, guided by knowledge on local-scale bio-morphodynamic feedbacks, cannot mitigate estuarine mud-infilling and restore antecedent sandy ecosystems. Unexpectedly, removal of mangroves enhances estuary-scale sediment trapping due to altered sedimentation patterns. Only reductions in upstream sediment supply can limit estuarine muddification. Our study demonstrates that bio-morphodynamic feedbacks can have contrasting effects at local and estuary scales. Consequently, human interventions like vegetation removal can lead to counterintuitive responses in estuarine landscape behavior that impede restoration efforts, highlighting that more holistic management approaches are needed. | ||
|CSDMS meeting posterPDF= Xie2023_EstuarineMangroves_UU4.pdf | |||
|CSDMS meeting posterPNG= Xie2023_EstuarineMangroves_UU4.png | |||
}} | }} | ||
{{blank line template}} | {{blank line template}} | ||
Latest revision as of 11:24, 12 May 2023
(if you haven't already)
"MA" is not in the list (NO STATE, Alabama, Alaska, Arizona, Arkansas, California, Colorado, Connecticut, D.C., Delaware, ...) of allowed values for the "CSDMS meeting state" property.
Log in (or create account for non-CSDMS members)
Forgot username? Search or email:CSDMSweb@colorado.edu
Browse abstracts
Missing the forest for the trees: how focusing on local bio-morphodynamic feedbacks compromises estuary-scale coastal management
Danghan Xie,
Boston University Boston , United States. danghan@bu.edu
Christian Schwarz, KU Leuven Leuven , Belgium.
Maarten Kleinhans, Utrecht University Utrecht , Netherlands.
Karin Bryan, University of Waikato Hamilton , New Zealand.
Giovanni Coco, University of Auckland Auckland , New Zealand.
Stephen Hunt, Waikato Regional Council Hamilton , New Zealand.
Barend van Maanen, University of Exeter Exeter , United Kingdom.
Changes in upstream land-use have significantly transformed downstream coastal ecosystems around the globe. Restoration of coastal ecosystems often focuses on local-scale processes, thereby overlooking landscape-scale interactions that can ultimately determine restoration outcomes. Here we use an idealized bio-morphodynamic model, based on estuaries in New Zealand, to investigate the effects of both increased sediment inputs caused by upstream deforestation following European settlement and mangrove removal on estuarine morphology. Our results show that coastal mangrove removal initiatives, guided by knowledge on local-scale bio-morphodynamic feedbacks, cannot mitigate estuarine mud-infilling and restore antecedent sandy ecosystems. Unexpectedly, removal of mangroves enhances estuary-scale sediment trapping due to altered sedimentation patterns. Only reductions in upstream sediment supply can limit estuarine muddification. Our study demonstrates that bio-morphodynamic feedbacks can have contrasting effects at local and estuary scales. Consequently, human interventions like vegetation removal can lead to counterintuitive responses in estuarine landscape behavior that impede restoration efforts, highlighting that more holistic management approaches are needed.