Template:TEXT BOX LEFT: Difference between revisions
From CSDMS
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
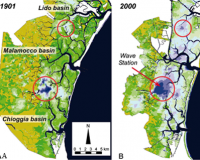
[[image: | [[image:Venice-point-tidal-flat.png|200px|left|link=Model_highlight#Modeling the Transition from Tidal Flat to Salt Marsh]] '''Modeling the Transition from Tidal Flat to Salt Marsh'''<br>Point Tidal Flat, a model developed by Dr. Sergio Fagherazzi, is a stochastic point model designed to simulate the geomorphic response of a tidal flat to variable rates of sediment resuspension caused by wind waves and import of sediment by tidal currents. The model explores the balance between erosion and deposition that occurs through time as bottom shear stresses change relative to tidal flat elevation. Point Tidal Flat has been used to demonstrate that the transition from tidal flat to salt marsh occurs abruptly, rather than continuously, when the sediment input reaches a critical value related to the local wind climate and fetch length of a specific basin. [[Model_highlight#Modeling the Transition from Tidal Flat to Salt Marsh|More...]]<br><br>[mailto:csdmsweb@colorado.edu Nominate a model] | ||
Revision as of 09:51, 31 August 2012
Modeling the Transition from Tidal Flat to Salt Marsh
Point Tidal Flat, a model developed by Dr. Sergio Fagherazzi, is a stochastic point model designed to simulate the geomorphic response of a tidal flat to variable rates of sediment resuspension caused by wind waves and import of sediment by tidal currents. The model explores the balance between erosion and deposition that occurs through time as bottom shear stresses change relative to tidal flat elevation. Point Tidal Flat has been used to demonstrate that the transition from tidal flat to salt marsh occurs abruptly, rather than continuously, when the sediment input reaches a critical value related to the local wind climate and fetch length of a specific basin. More...
Nominate a model