Meeting:Abstract 2013 CSDMS meeting-012: Difference between revisions
(Created page with "{{CSDMS meeting 2013 not paid}} {{CSDMS meeting personal information template-2013 |CSDMS meeting first name=Phu |CSDMS meeting last name=Nguyen |CSDMS meeting institute=UC Ir...") |
m (WikiSysop moved page Temp:Abstract 2013 CSDMS meeting-012 to Meeting:Abstract 2013 CSDMS meeting-012 without leaving a redirect) |
||
| (4 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{CSDMS meeting personal information template-2013 | {{CSDMS meeting personal information template-2013 | ||
|CSDMS meeting first name=Phu | |CSDMS meeting first name=Phu | ||
| Line 14: | Line 13: | ||
}} | }} | ||
{{CSDMS meeting abstract title template-2013 | {{CSDMS meeting abstract title template-2013 | ||
|CSDMS meeting abstract title=Modeling the Upper Little Missouri River flash flood 2010 Using a Coupled Distributed Hydrologic and Hydraulic Model | |CSDMS meeting abstract title=Modeling the Upper Little Missouri River flash flood 2010 Using a Coupled Distributed Hydrologic and Hydraulic Model | ||
}} | |||
{{CSDMS meeting authors template | |||
|CSDMS meeting coauthor first name abstract=Soroosh | |||
|CSDMS meeting coauthor last name abstract=Sorooshian | |||
|CSDMS meeting coauthor institute / Organization=UC Irvine | |||
|CSDMS meeting coauthor town-city=Irvine | |||
|CSDMS meeting coauthor country=United States | |||
|State=California | |||
|CSDMS meeting coauthor email address=soroosh@uci.edu | |||
}} | |||
{{CSDMS meeting authors template | |||
|CSDMS meeting coauthor first name abstract=Kuolin | |||
|CSDMS meeting coauthor last name abstract=Hsu | |||
|CSDMS meeting coauthor institute / Organization=UC Irvine | |||
|CSDMS meeting coauthor town-city=Irvine | |||
|CSDMS meeting coauthor country=United States | |||
|State=California | |||
|CSDMS meeting coauthor email address=kuolinh@uci.edu | |||
}} | |||
{{CSDMS meeting authors template | |||
|CSDMS meeting coauthor first name abstract=Amir | |||
|CSDMS meeting coauthor last name abstract=AghaKouchak | |||
|CSDMS meeting coauthor institute / Organization=UC Irvine | |||
|CSDMS meeting coauthor town-city=Irvine | |||
|CSDMS meeting coauthor country=United States | |||
|State=California | |||
|CSDMS meeting coauthor email address=amir.a@uci.edu | |||
}} | |||
{{CSDMS meeting authors template | |||
|CSDMS meeting coauthor first name abstract=Brett | |||
|CSDMS meeting coauthor last name abstract=Sanders | |||
|CSDMS meeting coauthor institute / Organization=UC Irvine | |||
|CSDMS meeting coauthor town-city=Irvine | |||
|CSDMS meeting coauthor country=United States | |||
|State=California | |||
|CSDMS meeting coauthor email address=bsanders@uci.edu | |||
}} | }} | ||
{{CSDMS meeting abstract template | {{CSDMS meeting abstract template | ||
|CSDMS meeting abstract=Flash floods are among the most devastating natural hazards, which cause loss of life and severe economic damages. Modeling flash floods to provide warnings to the public to prevent/mitigate the impacts of this type of disaster is still challenging. A coupled model which consists of | |CSDMS meeting abstract=Flash floods are among the most devastating natural hazards, which cause loss of life and severe economic damages. Modeling flash floods to provide warnings to the public to prevent/mitigate the impacts of this type of disaster is still challenging. A coupled model which consists of the currently used Hydrology Laboratory - Research Distributed Hydrologic Model (HL-RDHM) at NWS and a high resolution hydraulic model (BreZo) has been developed for flash flood modeling purposes. The model employs HL-RDHM as a rainfall-runoff generator in coarse resolution to produce surface runoff which will be zoned into point source hydrographs at the sub-catchment outlets. With point source input, BreZo simulates the spatial distributions of water depth and velocity of the flow in the river/channel and flood plain. | ||
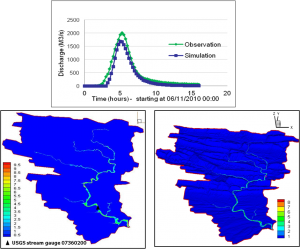
The model was utilized to investigate the historical flash flood event in the Upper Little Missouri River watershed, Arkansas. This event occurred on June 11th, 2010 and had killed 20 people and caused severe property damages. The catchment was divided into 55 sub-catchments based on Digital Elevation Model (DEM) at 10m resolution from USGS. From HL-RDHM surface runoff, 55 hydrographs can be derived, which then become 55 point sources as input in BreZo. The system was calibrated by tuning the roughness parameter in BreZo to best match the USGS discharge observation at the catchment outlet. The simulation results show the system performed very well not only for the total discharge at the catchment outlet but also the spatial distribution of the flash floods. | The model was utilized to investigate the historical flash flood event in the Upper Little Missouri River watershed, Arkansas. This event occurred on June 11th, 2010 and had killed 20 people and caused severe property damages. The catchment was divided into 55 sub-catchments based on Digital Elevation Model (DEM) at 10m resolution from USGS. From HL-RDHM surface runoff, 55 hydrographs can be derived, which then become 55 point sources as input in BreZo. The system was calibrated by tuning the roughness parameter in BreZo to best match the USGS discharge observation at the catchment outlet. The simulation results show the system performed very well not only for the total discharge at the catchment outlet (Nash-Sutcliffe efficiency = 0.91) but also the spatial distribution of the flash floods. | ||
}} | }} | ||
{{CSDMS meeting abstract figures | {{CSDMS meeting abstract figures | ||
|CSDMS meeting abstract figure= | |CSDMS meeting abstract figure=Picture1.png | ||
|CSDMS meeting abstract figure caption=Flooded map | |CSDMS meeting abstract figure caption=Discharge (m3/s) at USGS gauge 07360200 (top), Flooded map (m) (left) and Flow velocity (m/s) in 3-Dimensional view (right) | ||
}} | }} | ||
{{blank line template}} | {{blank line template}} | ||
Latest revision as of 10:58, 22 July 2015
Browse abstracts
Modeling the Upper Little Missouri River flash flood 2010 Using a Coupled Distributed Hydrologic and Hydraulic Model
[[Image:|300px|right|link=File:]]Flash floods are among the most devastating natural hazards, which cause loss of life and severe economic damages. Modeling flash floods to provide warnings to the public to prevent/mitigate the impacts of this type of disaster is still challenging. A coupled model which consists of the currently used Hydrology Laboratory - Research Distributed Hydrologic Model (HL-RDHM) at NWS and a high resolution hydraulic model (BreZo) has been developed for flash flood modeling purposes. The model employs HL-RDHM as a rainfall-runoff generator in coarse resolution to produce surface runoff which will be zoned into point source hydrographs at the sub-catchment outlets. With point source input, BreZo simulates the spatial distributions of water depth and velocity of the flow in the river/channel and flood plain.
The model was utilized to investigate the historical flash flood event in the Upper Little Missouri River watershed, Arkansas. This event occurred on June 11th, 2010 and had killed 20 people and caused severe property damages. The catchment was divided into 55 sub-catchments based on Digital Elevation Model (DEM) at 10m resolution from USGS. From HL-RDHM surface runoff, 55 hydrographs can be derived, which then become 55 point sources as input in BreZo. The system was calibrated by tuning the roughness parameter in BreZo to best match the USGS discharge observation at the catchment outlet. The simulation results show the system performed very well not only for the total discharge at the catchment outlet (Nash-Sutcliffe efficiency = 0.91) but also the spatial distribution of the flash floods.
| Discharge (m3/s) at USGS gauge 07360200 (top), Flooded map (m) (left) and Flow velocity (m/s) in 3-Dimensional view (right) |