CSDMS 2013 annual meeting poster Alan Howard
Simulating Fine-grained Alluvial Fan Sedimentation
Alex Morgan, University of Virginia Charlottesville Virginia, United States. amm5sy@virginia.edu
Abstract:
The majority of process studies on alluvial fans have focused on gravely fans. Many fan systems, however, are sourced from basins composed of fine-grained sediments. Deposition on such fans involves deposition from hyperconcentrated- or mud-flows. Many of such fans occur where there is sufficient vegetation to affect and, often, obscure depositional processes.
The modeling effort to be presented is motivated by the occurrence of fine-grained alluvial fans on Mars that feature a network of distributaries floored with coarser sediment and what we interpret to be fine-grained overbank deposits that comprise the bulk of the sediment. We have identified active fine grained fans in the arid Atacama desert deriving sediment from the higher Andes and lowland deposition dominated by muddy sheetflow sediment.
We are constructing a simulation model for deposition on such fans based on the fan-delta model of Sun et al. (2002). The model routes water and sediment through multiple distributaries that can branch, recombine, and avulse. Modeling flow and bedload sediment through the distributaries is relatively straightforward, but overbank deposition and avulsion processes are more problematic to characterize realistically (e.g. avoiding development of "holes" in fans or preventing evolution to a fixed distributary pattern). Our observation of overbank processes on the Atacama fans demonstrates the importance of sedimentation by long shallow sheetflow floods in addition to local levee aggradation. These processes are being implemented into our fan model.
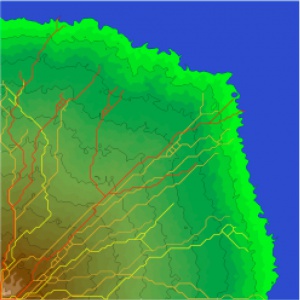 |
| * Please acknowledge the original contributors when you are using this material. If there are any copyright issues, please let us know and we will respond as soon as possible. |

