BMI: Difference between revisions
From CSDMS
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
<!-- ============================================= --> | <!-- ============================================= --> | ||
== {{ Bar Heading| text=Fine-grained Control Functions}} == | == {{ Bar Heading| text=Fine-grained Control Functions}} == | ||
: | : | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang=sidl> | <syntaxhighlight lang=sidl> | ||
| Line 13: | Line 11: | ||
void run_model (in string config_file) // Do a complete model run. Not needed for CMI. | void run_model (in string config_file) // Do a complete model run. Not needed for CMI. | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
: | |||
* These BMI functions are critical to plug-and-play modeling because they allow a calling component to bypass a model's own time loop. They also provide the caller with fine-grained control over the model, similar to a TV remote control. | |||
<br/> | <br/> | ||
<!-- ============================================= --> | <!-- ============================================= --> | ||
== {{ Bar Heading| text=Model Information Functions}} == | == {{ Bar Heading| text=Model Information Functions}} == | ||
: | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang=sidl> | |||
array<string> get_input_var_names() | |||
array<string> get_output_var_names() | |||
string get_attribute( in string att_name ) // (for model_name, mesh_type, time_step_type, etc.) | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
: | : | ||
* These BMI functions are called by the CSDMS framework in order to determine what input variables each model component needs and what output variables it can provide to other components. | * These BMI functions are called by the CSDMS framework in order to determine what input variables each model component needs and what output variables it can provide to other components. | ||
| Line 33: | Line 39: | ||
:as described below. For the "time_step_type" attribute, the allowed return values are: | :as described below. For the "time_step_type" attribute, the allowed return values are: | ||
fixed, adaptive, local | fixed, adaptive, local | ||
<br/> | <br/> | ||
<!-- ============================================= --> | <!-- ============================================= --> | ||
== {{ Bar Heading| text=Variable Information Functions}} == | == {{ Bar Heading| text=Variable Information Functions}} == | ||
: | : | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang=sidl> | <syntaxhighlight lang=sidl> | ||
| Line 60: | Line 56: | ||
double get_end_time() | double get_end_time() | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
: | |||
* These BMI functions are called by the CSDMS framework to obtain information about a particular input or output variable. Based on this information, the framework can apply type or unit conversion when necessary. | |||
* Note that "long variable name" and "long_var_name" refer to standardized variable names from the [[CSDMS_Standard_Names | '''CSDMS Standard Names''']]. | |||
'''GET_VAR_TYPE''': Return data type of a variable as a string. Some possible values are given in the following table. | '''GET_VAR_TYPE''': Return data type of a variable as a string. Some possible values are given in the following table. | ||
Revision as of 16:58, 5 September 2012
CSDMS Basic Modeling Interface (version 1.0)
Fine-grained Control Functions
void initialize (in string config_file)
void update (in double dt) // Advance model variables by time interval, dt (dt=-1 means use model time step)
void finalize ()
void run_model (in string config_file) // Do a complete model run. Not needed for CMI.- These BMI functions are critical to plug-and-play modeling because they allow a calling component to bypass a model's own time loop. They also provide the caller with fine-grained control over the model, similar to a TV remote control.
Model Information Functions
array<string> get_input_var_names()
array<string> get_output_var_names()
string get_attribute( in string att_name ) // (for model_name, mesh_type, time_step_type, etc.)- These BMI functions are called by the CSDMS framework in order to determine what input variables each model component needs and what output variables it can provide to other components.
- Note that "long variable name" and "long_var_name" refer to standardized variable names from the CSDMS Standard Names.
- The get_input_var_names() function returns a string array of the model's input variable names as "long variable names". Similarly, the get_output_var_names() function returns a string array of the models output variable names.
- The get_attribute() function is passed an attribute name from the following list:
model_name author_name mesh_type time_step_type
- and returns a corresponding string. For the "mesh_type" attribute, the allowed return values are:
uniform, rectilinear, s_mesh and u_mesh
- as described below. For the "time_step_type" attribute, the allowed return values are:
fixed, adaptive, local
Variable Information Functions
string get_var_type( in string long_var_name ) // ( returns type_string, e.g. ‘double’)
string get_var_units( in string long_var_name ) // ( returns unit_string, e.g. ‘meters’ )
int get_var_rank( in string long_var_name ) // ( returns array rank or 0 for scalar)
string get_var_name( in string long_var_name ) // ( returns model’s internal, short name )
double get_time_step() // (returns the model’s current timestep; adaptive or fixed.)
string get_time_units() // (returns unit string for model time, e.g. ‘seconds’, ‘years’)
double get_start_time()
double get_current_time()
double get_end_time()- These BMI functions are called by the CSDMS framework to obtain information about a particular input or output variable. Based on this information, the framework can apply type or unit conversion when necessary.
- Note that "long variable name" and "long_var_name" refer to standardized variable names from the CSDMS Standard Names.
GET_VAR_TYPE: Return data type of a variable as a string. Some possible values are given in the following table.
| BMI datatype | C datatype |
|---|---|
| BMI_CHAR | char |
| BMI_UNSIGNED_CHAR | unsigned char |
| BMI_INT | signed int |
| BMI_LONG | signed long int |
| BMI_UNSIGNED | unsigned int |
| BMI_UNSIGNED_LONG | unsigned long int |
| BMI_FLOAT | float |
| BMI_DOUBLE | double |
Variable Getter and Setter Functions
double get_0d_double( in string long_var_name )
array<double> get_1d_double( in string long_var_name )
array<double,2> get_2d_double( in string long_var_name )
array<double> get_2d_double_at_indices( in string long_var_name, array<int> indices )
void set_0d_double( in string long_var_name, in double scalar )
void set_1d_double( in string long_var_name, in array<double> array)
void set_2d_double( in string long_var_name, in array<double,2> array)
void set_2d_double_at_indices( in string long_var_name, in array<int> indices, in array<double,2> array)
Grid Information Functions
- The BMI function call get_attribute( 'mesh_type' ) should return one of the following strings:
uniform (for uniform rectilinear) rectilinear s_mesh (for structured mesh) u_mesh (for unstructured mesh)
- Each of these strings corresponds to a particular type of model grid or mesh. In order to provide a complete and standardized description of a model's grid, there is a different set of BMI functions that are required for each model "mesh_type" as described in this section.
- Note that an "orthogonal curvilinear" coordinate system is a special case of a "structured mesh".
- Note that "uniform rectilinear", "rectilinear" and "structured mesh" all have the topology of a two-dimensional array.
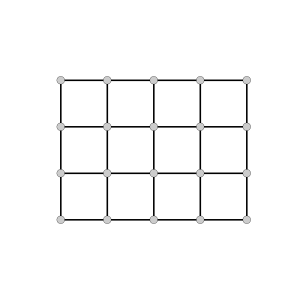
Uniform Rectilinear
array<double, 1> get_grid_spacing (in string long_var_name)
array<double, 1> get_grid_lower_left_corner (in string long_var_name)
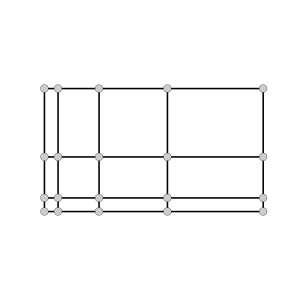
array<int, 1> get_grid_shape (in string long_var_name)Rectilinear
array<double, 1> get_grid_x (in string long_var_name)
array<double, 1> get_grid_y (in string long_var_name)
array<double, 1> get_grid_z (in string long_var_name)
array<int, 1> get_grid_shape (in string long_var_name)Structured Mesh
array<double, 1> get_grid_x (in string long_var_name)
array<double, 1> get_grid_y (in string long_var_name)
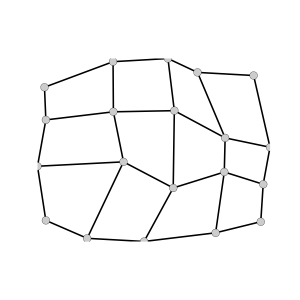
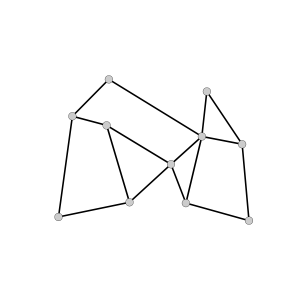
array<int, 1> get_grid_shape (in string long_var_name)Unstructured Mesh
array<double, 1> get_grid_x (in string long_var_name)
array<double, 1> get_grid_y (in string long_var_name)
array<int, 1> get_grid_connectivity (in string long_var_name)
array<int, 1> get_grid_offset (in string long_var_name)