CMI Description: Difference between revisions
From CSDMS
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
* The relationship between BMI and CMI is illustrated by the following diagram. | * The relationship between BMI and CMI is illustrated by the following diagram. | ||
: | : | ||
[[File:BMI_CMI_Image.png| | [[File:BMI_CMI_Image.png|500px|thumb|left]] | ||
* The CMI-wrapper calls a model's BMI functions. Based on the information that it gets from the Model Information Functions, it can determine whether it needs to call Service Components to adjust for differences between a given component model and other model component that it intends to share data with. The Service Components can adjust for differences in (1) the type of computational grid (regridding), (2) the time-stepping scheme, (3) variable names and (4) variable units. The CMI wrapper also uses Service Components to write model output in a standardized way to NetCDF files. | |||
Revision as of 16:05, 24 September 2012
CSDMS Component Model Interface (version 1.0)
- Any model that provides the Basic Model Interface (BMI) functions can be easily converted to a CSDMS plug-and-play component that has a CSDMS Component Model Interface or CMI. This conversion/wrapping process is done by CSDMS staff. The BMI functions are called by the CMI, by the framework and by service components. It is not necessary for a developer to learn anything about the CMI unless they're just curious.
- There is really only one CMI wrapper for each of the programming languages supported by CSDMS (C, C++, Fortran (all years), Java and Python). It can be thought of as a "harness" that "slips onto" a BMI-enabled model.
- The relationship between BMI and CMI is illustrated by the following diagram.
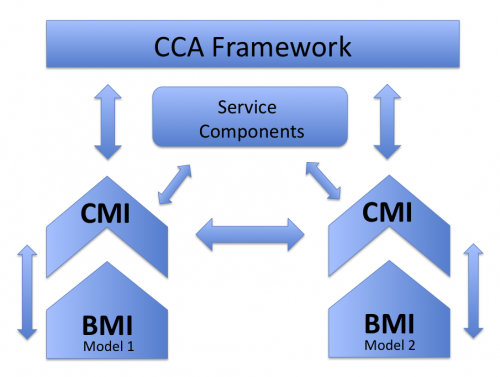
- The CMI-wrapper calls a model's BMI functions. Based on the information that it gets from the Model Information Functions, it can determine whether it needs to call Service Components to adjust for differences between a given component model and other model component that it intends to share data with. The Service Components can adjust for differences in (1) the type of computational grid (regridding), (2) the time-stepping scheme, (3) variable names and (4) variable units. The CMI wrapper also uses Service Components to write model output in a standardized way to NetCDF files.
