CSDMS Web Modeling Tool: Difference between revisions
Create high-level WMT page |
m Fix typo |
||
| (17 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
__NOTOC__ | __NOTOC__ | ||
[[File:WMT-3-views.png|600px|right]] | <div class=AutoScaleImage>[[File:WMT-3-views.png|600px|right]]<div> | ||
The CSDMS Web Modeling Tool, | The CSDMS Web Modeling Tool, | ||
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
* Download simulation results | * Download simulation results | ||
WMT provides a standardized graphical interface | |||
for components created from models | |||
submitted to the [[Model_download_portal|CSDMS Model Repository]]. | |||
To see how you can use WMT to configure and run a coupled model on the web, | To see how you can use WMT to configure and run a standalone or a coupled model on the web, | ||
check out the [[WMT_tutorial|WMT tutorial]], | check out the [[WMT_tutorial|WMT tutorial]], | ||
or jump right into using WMT at https://csdms.colorado.edu/wmt. | or jump right into using WMT at https://csdms.colorado.edu/wmt. | ||
== The architecture of WMT == | |||
WMT consists of two applications, | |||
the ''WMT client'' and the ''WMT server''. | |||
In a RESTful application, the client and server are separated. | |||
The client (what the user sees) stores little information, making it portable. | |||
The server (where the work is done) isn’t concerned with actions in the client, making it scalable. | |||
The client and server communicate through HTTP GET and POST methods, | |||
using JSON to carry information. | |||
WMT is stateless: each message passed between the client and the server | |||
contains all the information needed to perform an action. | |||
The WMT client is an Ajax application written in Java with the [http://www.gwtproject.org GWT] toolkit. | |||
For deployment on the web, | |||
the GWT compiler translates Java code to optimized and obfuscated JavaScript. | |||
The WMT client is supported on Firefox, Chrome, Safari, and Internet Explorer. | |||
The WMT server, written in Python and SQLite, is a layered system, | |||
with each layer exposing a web service API: | |||
* wmt-db: database of component, model, and simulation metadata and output | |||
* wmt-api: configure and connect components | |||
* wmt-exe: launch simulations on remote execution servers | |||
The database server provides JSON-encoded metadata for users to couple model components, | |||
including descriptions of component exchange items, uses and provides ports, and input parameters. | |||
Execution servers are network-accessible computational resources, | |||
ranging from HPC systems to desktop computers, | |||
containing the CSDMS software stack for running a simulation. | |||
Once a simulation completes, its output, in NetCDF, is packaged and uploaded to a data server | |||
where it is stored and from which a user can download it as a single compressed archive file. | |||
== A tool for the community == | |||
WMT was designed for use by the CSDMS community. | |||
If you encounter any problems in using WMT, | |||
or if you'd like to leave us feedback or suggestions for improvement, | |||
please email the CSDMS software engineers | |||
at [mailto:CSDMSsupport@colorado.edu CSDMSsupport@colorado.edu]. | |||
WMT is an MIT-licensed open source application, | WMT is an MIT-licensed open source application, | ||
built entirely with open source software | built entirely with open source software. | ||
The WMT source code is freely available on GitHub. | The WMT source code is freely available on GitHub. | ||
We actively encourage CSDMS members to contribute to the development of WMT | We actively encourage CSDMS members to contribute to the development of WMT | ||
by forking and cloning its GitHub repositories, | by forking and cloning its GitHub repositories, | ||
then sending pull requests with improvements back to the CSDMS | then sending pull requests with improvements back to the CSDMS software engineers. | ||
== Links == | == Links == | ||
| Line 39: | Line 81: | ||
* The WMT landing page is https://csdms.colorado.edu/wmt | * The WMT landing page is https://csdms.colorado.edu/wmt | ||
* The CSDMS wiki hosts the [[WMT_help|WMT help]] page and a [[WMT_tutorial|WMT tutorial]] | * The CSDMS wiki hosts the [[WMT_help|WMT help]] page and a [[WMT_tutorial|WMT tutorial]] | ||
* The source code for WMT can be found in | * The [[WMT_1.0_release|WMT 1.0]] and [[WMT_1.1_release|WMT 1.1]] release announcements | ||
** '''wmt''', the data/database server: https://github.com/csdms/wmt | * [[User:Mpiper|Mpiper]] presented a [[:File:Wmt-poster.pdf|poster]] on WMT at the 2015 AGU Fall Meeting | ||
* Other [[Tools_portal|modeling tools]] produced by CSDMS | |||
* The source code for WMT can be found in these GitHub repositories: | |||
** '''wmt-api''', the data/database server and API: https://github.com/csdms/wmt | |||
** '''wmt-exe''', the execution server: https://github.com/csdms/wmt-exe | ** '''wmt-exe''', the execution server: https://github.com/csdms/wmt-exe | ||
** '''wmt-client''', the web client: https://github.com/csdms/wmt-client | ** '''wmt-client''', the web client: https://github.com/csdms/wmt-client | ||
* | ** '''wmt-metadata''', metadata for components: https://github.com/csdms/wmt-metadata | ||
--[[User:Mpiper|Mpiper]] ([[User talk:Mpiper|talk]]) 14:26, 13 October 2016 (MDT) | --[[User:Mpiper|Mpiper]] ([[User talk:Mpiper|talk]]) 14:26, 13 October 2016 (MDT) | ||
Latest revision as of 16:53, 20 September 2018
The CSDMS Web Modeling Tool
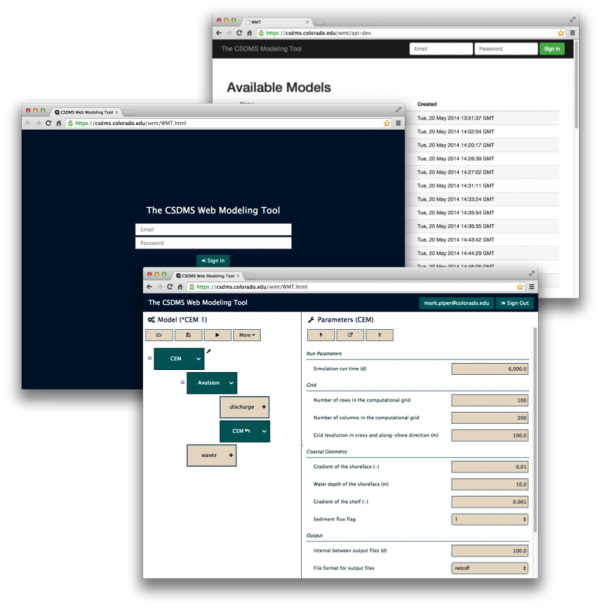
The CSDMS Web Modeling Tool, WMT, is a web application that provides an Ajax client-side graphical interface and a RESTful server-side database and API that allows users, from a web browser on a desktop, laptop or tablet computer, to build and run coupled surface dynamics models on a supercomputer.
With WMT, users can:
- Design a model from a set of components
- Edit component parameters
- Save models to a web-accessible server
- Share saved models with the community
- Submit runs to an HPC system
- Download simulation results
WMT provides a standardized graphical interface for components created from models submitted to the CSDMS Model Repository.
To see how you can use WMT to configure and run a standalone or a coupled model on the web, check out the WMT tutorial, or jump right into using WMT at https://csdms.colorado.edu/wmt.
The architecture of WMT
WMT consists of two applications, the WMT client and the WMT server.
In a RESTful application, the client and server are separated. The client (what the user sees) stores little information, making it portable. The server (where the work is done) isn’t concerned with actions in the client, making it scalable. The client and server communicate through HTTP GET and POST methods, using JSON to carry information. WMT is stateless: each message passed between the client and the server contains all the information needed to perform an action.
The WMT client is an Ajax application written in Java with the GWT toolkit. For deployment on the web, the GWT compiler translates Java code to optimized and obfuscated JavaScript. The WMT client is supported on Firefox, Chrome, Safari, and Internet Explorer.
The WMT server, written in Python and SQLite, is a layered system, with each layer exposing a web service API:
- wmt-db: database of component, model, and simulation metadata and output
- wmt-api: configure and connect components
- wmt-exe: launch simulations on remote execution servers
The database server provides JSON-encoded metadata for users to couple model components, including descriptions of component exchange items, uses and provides ports, and input parameters. Execution servers are network-accessible computational resources, ranging from HPC systems to desktop computers, containing the CSDMS software stack for running a simulation. Once a simulation completes, its output, in NetCDF, is packaged and uploaded to a data server where it is stored and from which a user can download it as a single compressed archive file.
A tool for the community
WMT was designed for use by the CSDMS community. If you encounter any problems in using WMT, or if you'd like to leave us feedback or suggestions for improvement, please email the CSDMS software engineers at CSDMSsupport@colorado.edu.
WMT is an MIT-licensed open source application, built entirely with open source software. The WMT source code is freely available on GitHub. We actively encourage CSDMS members to contribute to the development of WMT by forking and cloning its GitHub repositories, then sending pull requests with improvements back to the CSDMS software engineers.
Links
- The WMT landing page is https://csdms.colorado.edu/wmt
- The CSDMS wiki hosts the WMT help page and a WMT tutorial
- The WMT 1.0 and WMT 1.1 release announcements
- Mpiper presented a poster on WMT at the 2015 AGU Fall Meeting
- Other modeling tools produced by CSDMS
- The source code for WMT can be found in these GitHub repositories:
- wmt-api, the data/database server and API: https://github.com/csdms/wmt
- wmt-exe, the execution server: https://github.com/csdms/wmt-exe
- wmt-client, the web client: https://github.com/csdms/wmt-client
- wmt-metadata, metadata for components: https://github.com/csdms/wmt-metadata
