Tools portal
Tools
CSDMS-IF (and maybe community?) has developed tools for the community to use. We should at least mention for each of our tools the following:
- why to use tools (how does a tool help them in their research),
- how to use the tools,
- where to get more information on the tools,
- how to report bugs, ....
- you name it.
I put your name down below each tool that needs more info. Maybe each tools needs its own page that links from this page, so the items below are really just a placeholder.
So type away, focus less on layout more on content right now maybe?
Thanks, A.
BMI
Eric
BMI builder
Eric
BMI tester
Eric
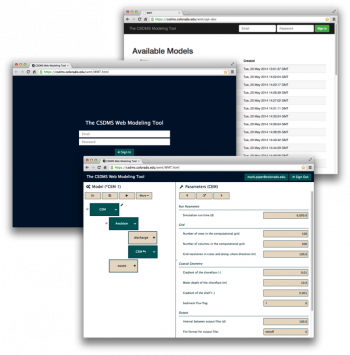
WMT
The CSDMS Web Modeling Tool, WMT, is a web application that provides an Ajax client-side graphical interface and a RESTful server-side database and API that allows users, from a web browser on a desktop, laptop or tablet computer, to build and run standalone or coupled Earth surface dynamics models on a supercomputer.
With WMT, users can:
- Design a model from a set of CSDMS components
- Edit model parameters
- Save models to a web-accessible server
- Share saved models with the community
- Submit model runs to an HPC system
- Download simulation results
To see how you can use WMT to configure and run a standalone or a coupled model on the web,
check out the WMT tutorial,
or jump right into using WMT at https://csdms.colorado.edu/wmt.
For more information on WMT, including links to its documentation and its source code repositories, please see the CSDMS Web Modeling Tool wiki page.
PyMT
pymt is an Open Source Python package that provides the tools needed to run and couple models that expose the Basic Model Interface (BMI).
pymt contains:
- Tools necessary for coupling models of disparate time and space scales (including grid mappers)
- Time-steppers that coordinate the sequencing of coupled models
- Exchange of data between BMI-enabled models
- Wrappers that automatically load BMI-enabled models into the PyMT framework
- Utilities that support open-source interfaces (UGRID, SGRID, CSDMS Standard Names, etc.)
- A collection of community-submitted models, written in a variety of programming languages, from a variety of process domains -- but all usable from within the Python programming language
- A plug-in framework for adding additional BMI-enabled models to the framework
pymt is an element of the CSDMS Workbench, an integrated system of software tools, technologies, and standards for building and coupling models.
Available models and tools in pymt
| Program | Description | Developer | Download | PyMT |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Avulsion
|
Stream avulsion model | Hutton, Eric | ||
| CEM | Coastline evolution model | Murray, A. Brad | ||
| CHILD | Landscape Evolution Model | Tucker, Greg | ||
DepthDependentDiffuser
|
Soil depth-dependent linear hillslope diffuser | Glade, Rachel | ||
| ECSimpleSnow | A simple snow model | Wang, Kang | ||
ErosionDeposition
|
Landlab component for fluvial erosion/deposition. | Shobe, Charles | ||
Frost Model
|
Frost model predicts the likelihood of occurrence of permafrost in the land surface based on the monthly temperature distribution | Overeem, Irina | ||
| GIPL | GIPL(Geophysical Institute Permafrost Laboratory) is an implicit finite difference one-dimensional heat flow numerical model. | Jafarov, Elchin | ||
GeoTiff Data Component
|
A CSDMS data component for accessing data and metadata from a GeoTIFF file, through either a local filepath or a remote URL.. | Piper, Mark | ||
GridMET Data Component
|
A CSDMS data component for fetching and caching gridMET meteorological data. | McDonald, Rich | ||
| HydroTrend | Climate driven hydrological transport model | Kettner, Albert | ||
Kudryavtsev Model
|
Permafrost Active Layer Thickness Model based on Kudryavtsev's parametrization | Overeem, Irina | ||
| NWM Data Component | A CSDMS data component used to download the National Water Model datasets. | Gan, Tian | ||
OverlandFlow
|
Component simulating overland flow using a 2-D numerical approximation of the shallow-water equations following the de Almeida et al., 2012 algorithm for storage-cell inundation modeling. | Adams, Jordan | ||
| Plume | Hypopycnal sediment plume | Hutton, Eric | ||
RAFEM
|
River Avulsion and Floodplain Evolution Module | Ratliff, Katherine | ||
SPACE
|
Landlab component for 2-D calculation of fluvial sediment transport and bedrock erosion | Shobe, Charles | ||
| Sedflux | Basin filling stratigraphic model | Hutton, Eric | ||
| Subside | Flexure model | Hutton, Eric | ||
Topography Data Component
|
A CSDMS data component used to fetch and cache NASA Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM) and JAXA Advanced Land Observing Satellite (ALOS) land elevation data using the OpenTopography REST API. | Piper, Mark |
Resources
- Documentation, both for users and developers, can be found at https://pymt.readthedocs.io
- The pymt source code is on GitHub: https://github.com/csdms/pymt. Go there to contribute to pymt, ask a pymt-related question, or submit an issue.
- Examples of using pymt (Jupyter Notebooks)
Dakotathon
Dakota is a software toolkit developed at Sandia National Laboratories that provides an interface between models and a library of analysis methods, including support for sensitivity analysis, uncertainty quantification, optimization, and calibration techniques. Dakota is a powerful tool, but its learning curve is steep: the user not only must understand the structure and syntax of the Dakota input file, but also must develop intermediate code that allows Dakota to set up and run a model, read outputs from the model, and calculate a response statistic from the outputs.
The CSDMS Dakota Interface, or Dakotathon, is a Python package that wraps and extends Dakota’s file-based user interface. It simplifies the process of configuring and running a Dakota experiment, and it allows a Dakota experiment to be scripted. Dakotathon creates the Dakota input file and provides a generic analysis driver. Any model componentized in the CSDMS modeling framework automatically works with Dakotathon. Dakotathon has a plugin architecture, so models not wrapped into the CSDMS modeling framework can be accessed by Dakotathon by programmatically extending a template; an example is provided in the Dakotathon distribution.
For more information on Dakotathon,
including links to its documentation and its source code repository,
please see the Dakotathon wiki page.