Labs WMT Ganges Sediment Supply: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Modeling the Future Sediment Flux of the Ganges River with HydroTrend== | ==Modeling the Future Sediment Flux of the Ganges River with HydroTrend== | ||
'''Introduction''' | |||
The Ganges-Brahmaputra Delta is one of the largest deltas in the world. In Bangladesh alone, 160 million people live in the floodplains. The Ganges and Brahmaputra Rivers and their delta are strongly impacted by the Asian summer monsoon. Widespread hazards relate to the intense seasonal rainfall: flooding, river erosion and channel switches. The people of Bangladesh have adapted to this dynamic delta system, they have raised villages above the annual flood level and embanked agricultural land.<br> | The Ganges-Brahmaputra Delta is one of the largest deltas in the world. In Bangladesh alone, 160 million people live in the floodplains. The Ganges and Brahmaputra Rivers and their delta are strongly impacted by the Asian summer monsoon. Widespread hazards relate to the intense seasonal rainfall: flooding, river erosion and channel switches. The people of Bangladesh have adapted to this dynamic delta system, they have raised villages above the annual flood level and embanked agricultural land.<br> | ||
| Line 8: | Line 7: | ||
At the same time, the Ganges-Brahmaputra river system drains tremendous amounts of sediment (sand, silt and clay) from its steep Himalayan hinterland. We ask: how does this amount of sediment change with a changing monsoonal climate? Does this sediment aggrade fast enough to help counteract rapid sea-level rise? <br><br> | At the same time, the Ganges-Brahmaputra river system drains tremendous amounts of sediment (sand, silt and clay) from its steep Himalayan hinterland. We ask: how does this amount of sediment change with a changing monsoonal climate? Does this sediment aggrade fast enough to help counteract rapid sea-level rise? <br><br> | ||
[[File:GangesMap.png|600px]] | [[File:GangesMap.png|600px]] | ||
'''Classroom Organization''' | |||
This lab investigates 1) the modeling of the incoming water and sediment load of the Ganges river, 2) the validity of model output compared to real-world observations, and 3) how future changes in the monsoon possibly affect this sedimentary system and 4) we try to assess the uncertainty of such predictions. | This lab investigates 1) the modeling of the incoming water and sediment load of the Ganges river, 2) the validity of model output compared to real-world observations, and 3) how future changes in the monsoon possibly affect this sedimentary system and 4) we try to assess the uncertainty of such predictions. | ||
This lab will run HydroTrend simulation with Python Modeling Tool (Pymt). If you have never used the Pymt, learn how to use it [https://pymt.readthedocs.io/en/latest/install.html here]. The Pymt allows you to set up simulations and run notebooks. | |||
If you are a faculty at an academic institution, it is possible to work with us to get temporary teaching accounts. Work directly with us by emailing: csdms@colorado.edu | |||
'''Learning objectives''' | |||
Skills | |||
*use Pymt to run HydroTrend Model | |||
*familiarize with a basic configuration of the HydroTrend Model | |||
*make small changes to key input parameters | |||
*hands-on experience with visualizing output in Python | |||
Key Concepts: | |||
*Simulation of the river discharge for Ganges River | |||
*Simulation of the suspended sediment discharge for Ganges River | |||
*What is the mean annual flow for Ganges River | |||
'''Lab Notes''' | |||
You can launch binder to directly run the Jupyter Notebook for this lab through a web browser. | |||
>> Open a new browser window and open the Pymt read the docs page [https://pymt.readthedocs.io/en/latest/examples.html here] | |||
<br> | >> You will see that there are several example models. In this lab we will select the HydroTrend model. <br> | ||
>> Click on the 'Launch Binder' box and it will allow you to see this lab as a Jupyter Notebook.<br> | |||
>> You can execute the Jupyter notebook code cells using shift -enter. | |||
Revision as of 14:29, 26 March 2020
Modeling the Future Sediment Flux of the Ganges River with HydroTrend
Introduction
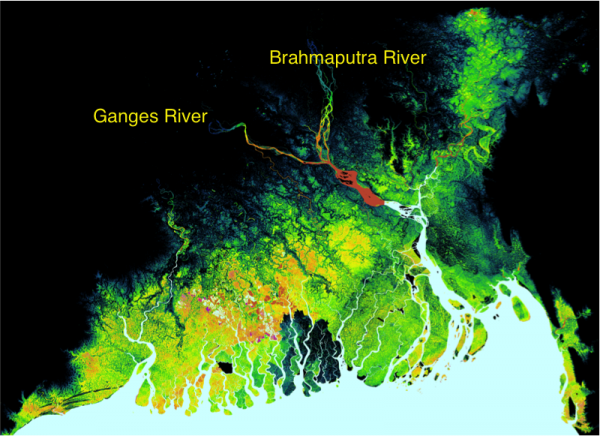
The Ganges-Brahmaputra Delta is one of the largest deltas in the world. In Bangladesh alone, 160 million people live in the floodplains. The Ganges and Brahmaputra Rivers and their delta are strongly impacted by the Asian summer monsoon. Widespread hazards relate to the intense seasonal rainfall: flooding, river erosion and channel switches. The people of Bangladesh have adapted to this dynamic delta system, they have raised villages above the annual flood level and embanked agricultural land.
Still, the lowlands of the Ganges-Brahmaputra Delta are considered one of the regions most at risk from climate change, and particularly from sea level rise. About 75 million people live in the GB coastal zone (defined as the region <10 m.a.s.l). It is thought that the impact of relative sea-level change will be profound in Bangladesh where 32% of the country is already affected by tides, salinization, and cyclones/storm surges.
At the same time, the Ganges-Brahmaputra river system drains tremendous amounts of sediment (sand, silt and clay) from its steep Himalayan hinterland. We ask: how does this amount of sediment change with a changing monsoonal climate? Does this sediment aggrade fast enough to help counteract rapid sea-level rise?
Classroom Organization
This lab investigates 1) the modeling of the incoming water and sediment load of the Ganges river, 2) the validity of model output compared to real-world observations, and 3) how future changes in the monsoon possibly affect this sedimentary system and 4) we try to assess the uncertainty of such predictions.
This lab will run HydroTrend simulation with Python Modeling Tool (Pymt). If you have never used the Pymt, learn how to use it here. The Pymt allows you to set up simulations and run notebooks.
If you are a faculty at an academic institution, it is possible to work with us to get temporary teaching accounts. Work directly with us by emailing: csdms@colorado.edu
Learning objectives
Skills
- use Pymt to run HydroTrend Model
- familiarize with a basic configuration of the HydroTrend Model
- make small changes to key input parameters
- hands-on experience with visualizing output in Python
Key Concepts:
- Simulation of the river discharge for Ganges River
- Simulation of the suspended sediment discharge for Ganges River
- What is the mean annual flow for Ganges River
Lab Notes
You can launch binder to directly run the Jupyter Notebook for this lab through a web browser.
>> Open a new browser window and open the Pymt read the docs page here
>> You will see that there are several example models. In this lab we will select the HydroTrend model.
>> Click on the 'Launch Binder' box and it will allow you to see this lab as a Jupyter Notebook.
>> You can execute the Jupyter notebook code cells using shift -enter.
