CSDMS 2016 annual meeting poster RaleighMartin
Linear scaling of wind-driven sand flux with shear stress
Jasper Kok, University of California, Los Angeles Los Angeles California, United States. jfkok@ucla.edu
Abstract:
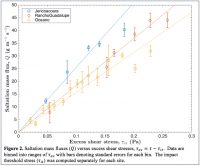
Wind-driven sand transport generates atmospheric dust and sculpts dunes, yet models for this process generally perform poorly. A paradigm underlying most such models is that particle speed increases linearly with wind shear velocity, resulting in the long-established nonlinear scaling of sand flux to the three-halves power of wind shear stress. Here, we present comprehensive measurements at three field sites showing that characteristic particle hop heights, and thus particle speeds, remain approximately constant with shear velocity. This result implies a linear dependence of wind-blown flux on wind shear stress, which we confirm by direct observation of the stress-flux relationship at all sites. Models for dust generation, dune migration, and other processes driven by wind-blown sand on Earth, Mars, and several other planetary surfaces should be modified to account for linear stress-flux scaling.
* Please acknowledge the original contributors when you are using this material. If there are any copyright issues, please let us know and we will respond as soon as possible.